Electromagnetic Navigation Bronchoscopy (ENB)-Guided Uniportal Video-Assisted Thoracic Surgery (VATS) for Lung Surgery

Owning to advances in diagnostic technology, imaging test such as a low-dose computed tomography (also called a low-dose CT scan) has become the recommended screening test for lung cancer. This diagnostic procedure uses a computer linked to an x-ray machine that emits a very low amount of radiation to make a series of detailed pictures of the lung. Displayed as 3D images, abnormal tumors in the lung can be detected, even smaller than 1 cm. in diameter. As a result, it allows for the early detection of lung cancer while the size of the tumor remains confined in its earliest stages which often exhibit no signs or symptoms. Early detection of lung cancer substantially leads to effective treatments conducted in a timely manner before the condition progresses to advanced stage presenting with metastasis in which cancerous cells spread to other parts of the body. According to the American Cancer Society, if lung cancer is identified at stage 1A1 – the tumor is 1 cm. or smaller, the chance of being cured for patients with non-small cell lung cancer represented as the five-year survival rate is about 92 percent.
Nevertheless, under most circumstances, it seems to be medically challenging to accurately diagnose detected lung tumors sized less than 1 cm, compared to larger lung masses. Diagnosis of lung cancer is usually confirmed with a lung biopsy. However, in some cases, transbronchial lung biopsy using flexible bronchoscopy with biopsy forceps and CT guided needle biopsy are not applicable since the lung nodules are located in a hard-to-reach spots. In such a case, surgical biopsy is considered the most effective diagnostic procedure to pathologically confirm the suspected masses in the lung.
As one of the surgical biopsy techniques, video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) has been extensively used for diagnosing and treating a variety of conditions involving the chest, including lung cancer. Uniportal VATS is a minimally invasive surgery that involves accessing the lungs through a single incision. Electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy (ENB) is an emerging option for guided bronchoscopy, deploying a 3-dimensional reconstruction of CT for a better accuracy.
Combined with the use of 4K surgical camera system, ENB-guided uniportal VATS has been performed by well-trained cardiothoracic surgeons at Bangkok Heart Hospital to treat lung cancer and other related conditions. Visualizing a suspicious tissue structure at close proximity is the key to assessing and operating successfully. With the 4K technology, clear and improved thoracoscopic visibility enables the cardiothoracic surgeons to accurately operate with high degree of safety, ensuring more precise and safe procedures. Particularly in patients presenting with lung nodules smaller than 1 cm. along with ground glass opacity (GGO) – the hazy gray areas that can show up in CT scans or X-rays of the lungs, electromagnetic navigation bronchoscopy can significantly aid in pinpointing the exact locations of those nodules, leading to appropriate interventions and treatments.
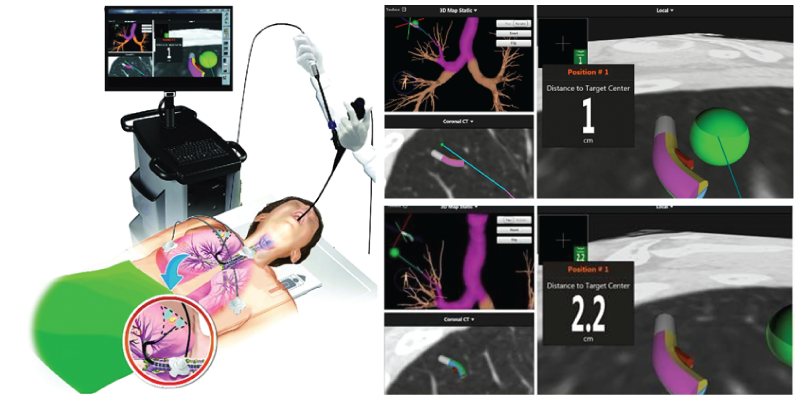
ENB –an innovative navigation technology can diagnose lung cancers earlier. This GPS-like technology (similar to Google Map) navigates through the central airway to sample suspicious lung lesions without invasive surgery. Devices used during the procedure include:
- Pre-loaded mapping derived from computed tomography (CT) scan of the lungs
- An electromagnetic field used to pinpoint the precise location of abnormal lung tissue
- Patient sensor triplet allowing precise tracking
- Locatable guide via bronchoscopy to track the location of the probe in the lungs
Prior to the procedure, the system uses the CT scan to create a virtual bronchial tree similar to a road map. Once the target lesion is identified, the system plans a pathway through the bronchial tree to reach the target. During the procedure, the electromagnetic field and locatable guide allows the computer to track the location of the probe in the lungs. The surgeon can then follow the pre-loaded mapping or pre-planned path through the bronchial tree to access the target location. With similar function to GPS navigation when driving, ENB enables the cardiothoracic surgeon to accurately reach and locate the suspicious lesions for further pathological investigations. In case those pathological results indicate the early stages of lung cancers, further lung resection such as lobectomy or segmentectomy with lymph node removal will be followed for proper treatment of lung cancers.